Industrial Water Desalination
Home » Water Desalination System » Industrial Water Desalination
This article will provide general information about water desalination devices, especially their industrial type. Understanding these concepts can help you make decisions when making a purchase. Sepahan Palayesh, a manufacturer of industrial desalination systems in Isfahan and other parts of Iran, can assist you in installing your industrial water desalination system. Stay with us to learn more about this technology.
The global water demand is more than ever and may increase significantly in the coming years. As a result, people should find solutions to problems such as water scarcity as soon as possible. Various devices have developed with advantages and disadvantages. One of the most popular devices is the industrial model of water desalination.
Do you know how these devices work and what are their components and features? If your answer is no, continue reading to learn more about this topic.
What is an Industrial water desalination?
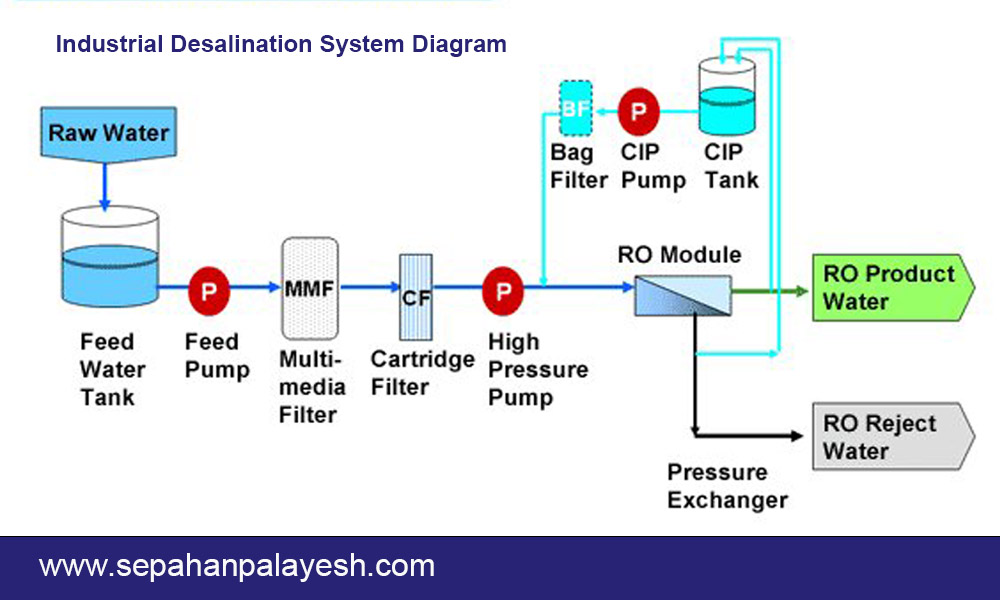
Industrial water desalination devices convert highly salty water, such as seawater and groundwater, into fresh water. These devices purify water through semi-permeable membrane processes. Large-scale water desalination is essential for providing water to regions facing a shortage of fresh water. Nowadays, the semi-permeable membrane process or reverse osmosis is one of the most cost-effective methods for industrial water purification. Industrial desalination devices are industrial Ro packages, industrial water purifiers, and reverse osmosis packages. They are designed to desalinate water with a volume of 5 cubic meters or more.

What is the reverse osmosis process?
When considering the purchase of an industrial water desalination system, it’s essential to understand the concept of reverse osmosis and how the device functions. Reverse osmosis is a pressure-based process that transfers pressure across a semi-permeable membrane to prevent small impurities from passing into the water. Typically, smaller industrial desalination units operate at lower pressures, around 35 psi. It’s important to note that industrial desalination water operating at less than 45 psi may not produce good quality water, and the device may have a problem.
When the water pressure entering the device is too low, it produces much less drinking water. That leads to slower filling of storage tanks and lower water quality. The pressure switch device monitors water pressure in reverse osmosis storage tanks. It turns the pump off and on based on the pressure in the tank. The most common pressure that causes the RO unit to turn off is 40 psi.
The hypothesis for this method was first proposed in 1748 by Jean-Anthony Nolte. Despite significant progress in the subsequent years, it was not enough to accomplish the task. Therefore, in 1949, researchers from the University of California made the first successful attempt at desalinating water with this method.
Industrial water desalination device equipment
The equipment for industrial water desalination devices aids in improving water purification processes. In the following section, we will briefly describe each of these components.
Types of industrial water desalination filters
Industrial water desalination systems have different filters. Each filter has its function. In the following, we describe their types:
- Carbon filters
Every industrial water desalination has high-quality carbon filters. Carbon filters are also known as taste and smell filters.
- Sand filters
This type of filter is designed to handle various kinds of pressure. The sand filter’s function is to eliminate suspended particles up to 50 microns in size. The layers of sand have different grain sizes, which allows them to separate easily during backwashing.
- Cartridge filters or micron filters
As the name suggests, this filter removes particles of sand, dirt, and sediment up to 5 microns.
- Nanofiltration
Nano filters eliminate all viruses well. This kind of filter will remove organic molecules, natural organic matter, and too much salt from water. Also, nano filters remove the ions that cause the water to harden. Therefore, these types of filters are mostly used to soften water.
- Ultrafiltration
When water passes through this filter, viruses remain, and many microorganisms are removed, because ultrafilters have 0.01-micron pores.
- Membrane
This type of filter is an essential component of industrial water purification systems. It can remove about 99.6% of solids from water. Reverse osmosis membranes consist of three layers that cover its surface. These layers include:
• Protective layer made of moisture-retaining polyester
• Thin polyamide layer
• The inner layer is composed of fine polysulfone
The life expectancy of the membranes is typically 2 to 3 years. However, their lifespan will extended with proper maintenance, suitable operating conditions, and timely acid washing.
Pressure chamber
This chamber is a pressure vessel containing membrane elements, called a pressure vessel, and can accommodate up to six membrane elements.
High-pressure pump
The high-pressure pump is a crucial component of the reverse osmosis system. The Murray Danfoss high-pressure piston pump is extensively used in industrial water desalination. While centrifugal pumps are also used, tests have shown that the high-pressure piston pump outperforms them. Its lightweight design allows for better arrangement within desalination plants.
Anti-fouling injection system
Anti-fouling chemicals are applied to industrial desalination membranes to prevent sedimentation and clogging and increase lifespan.
The proper pressure of industrial water desalination
The industrial water desalination package requires a specific pressure for the water purification process to produce fresh water. The optimal pressure for operation is about 60 psi. However, using a small pump to increase the pressure to 80 psi makes the device operate even more efficiently.
Types of industrial water desalination devices
There are different types of industrial water desalination devices.
- Pressure strainer and micro filter
This device removes mud and suspended substances and provides clear quality water. - Charcoal filter device
Charcoal filter devices remove color, turbidity, and chlorine in water.
- Water softener
Many substances cause water hardness. Among them are calcium and magnesium. Hardliners work to eliminate them.
- Deionizer device
The deionizer consists of cation and anion columns that remove cations and anions to produce pure water. - Reverse osmosis device
Another term for reverse osmosis is water desalination, which creates pure, iodine-free water. - Nanofiltration device
This device is designed to destroy all organic substances and microorganisms.
Types of industrial water purifier devices based on incoming water
- Well water purifier
This device, also known as a Brackish Well water, can purify and sweeten incoming raw water up to TDS 4000 PPM. - Surface salt water purifier
This device, also known as Brackish Surface Water, can purify incoming raw water up to TDS 000 PPM. - Sea water purifier
This device, called Sea Water, can purify incoming raw water up to TDS 000 PPM.
The water desalination device capacity
The capacity and volume of desalination devices vary based on the incoming water. For instance, industrial water desalination devices can process 5 to 25 cubic meters daily. Semi-industrial devices can produce 1400 to 5000 liters daily. Devices with a capacity exceeding 25 cubic meters use multiple membranes, each with a 25 cubic meter capacity.
Different designs of industrial water desalination
Industrial water desalination devices are designed based on the amount of salinity, the amount of water required for production, and their temperature in the form of single-pass or single-stage, two-pass or two-stage, single-stage or two-stage. In most cases, single-pass designs are very suitable for producing water. In the following, we will briefly explain each of them.
- Single-pass or single-stage
“Single-pass or single-stage” refers to a desalination design that produces desalinated water by one stage using a set of RO membranes. This design has limited application in seawater desalination due to the low quality of the produced water. Even with RO membranes with the highest salt removal rate, the water quality cannot reach a total dissolved solids (TDS) level of less than 200 mg. - Two-stages
A two-stage design enhances freshwater quality. In this design, the effluent from the first stage enters the second stage of reverse osmosis. The brine produced in the first stage has much lower pressure than the raw water inlet pressure of the first stage, which is enough to overcome the osmotic pressure of the second stage. However, if we try to recover it in the second stage of reverse osmosis, it will increase the salinity in the leachates. Therefore, this plan is mainly needed to maximize the use of raw water resources. - Double pass
The reverse osmosis double pass design involves transferring fresh water from the first stage to the second stage. This design combines elements of single-pass and single or multi-pass BWRO systems. The products from the first pass are sent to the BWRO system to produce water with fewer dissolved ions. This design is for very high salinity seawater or when strict quality standards for freshwater are required.
This design is cost-effective and features a unique layout and functionality.
Currently, devices or designs with two or more passes are appropriate for industrial water of very high purity.
Design an industrial water desalination device
Water desalination devices are complex systems that require careful consideration of factors such as water inlet and discharge pipes, drinking water pressure, and other design elements. To optimal performance, a reverse osmosis water purifier should remove 95 to 99% of water impurities. The effectiveness of the RO system is measured by its ability to remove salt and other impurities from water.
Several software programs simulate the design of water distillations with the reverse osmosis process. One of these programs is ROSA software. Another one developed by DOW is WAVE software. This software has fixed the defects of the previous software and designed all parts of industrial water treatment, including pre-treatment, reverse osmosis, ion exchange, and final treatment of all types of urban, well, and seawater. WAVE software has been developed to integrate and advance the capabilities of previous software.
Required parameters for Ro package design
• Water inlet flow rate
• The pressure of the water flow entering the device
• The flow of water treated by RO
• The temperature of the environment and the temperature of the water entering the device
• The pressure of the effluent flow from the industrial desalination device
• Electrical conductivity or EC that enters the water
• Fundamental indicators in industrial water desalination design
In preparing industrial water desalination devices, manufacturers consider a series of guidelines and indicators to be superior to other indicators, which are:
Raw water pressure
Determining the exact pressure of water entering the membranes and choosing a suitable pump requires the precision and expertise of designers in this field. With improper pressure and inadequacy of pumps, access to operational conditions becomes difficult and costly.
Passing flux of the membrane
The amount and intensity of the flow of freshwater that passes through the surface of the membrane is called flux. In the design of the reverse osmosis process, choosing a suitable flux is very important. If the flux is inappropriate, it will reduce the quality of water and membrane lifespan and increase operational and repair costs. When choosing an appropriate flux, it is essential to consider the raw water quality, the type of membrane, and pre-treatment.
Choosing the type of membrane
Several factors are considered when selecting a membrane, making it challenging to choose the right one.
The percentage of recycled freshwater
The percentage of recycled freshwater depends on various factors, such as the number of membranes in use, environmental considerations for leachate disposal, operational conditions, and the analysis of inlet water.
Purification process in industrial water desalination devices
Industrial water desalination devices utilize reverse osmosis technology and multimedia filters to convert saltwater into freshwater and remove particles larger than 10 microns. That process involves injecting an anti-coagulant chemical into the water to control its hardness and ensure the health of the membranes. The Pre-treatment eliminates hardness, chlorine, color, odor, and sulfur. The water then proceeds to the reverse osmosis components for further purification.
During this phase of the purification process, a high-pressure pump exerts pressure on the solution. This pressure helps to separate the remaining salts and impurities. As a result, clean and safe drinking water is produced from the membrane, while salts, minerals, and other impurities are expelled from the other side. Subsequently, the water undergoes sterilization to eliminate any remaining bacteria and microbes.
- Pre-treatment Processes
Various technologies and processes are used in the pre-treatment, selected based on chemical, physical, and biological microbial analysis of the saltwater. The most common method used in the pre-treatment of industrial desalination include the following: - Carbon process and sand bed
These two methods are some of the oldest water treatment processes. They are designed in two different ways, using gravity and pressure. The choice between these methods depends on the water analysis and the specific conditions of the water treatment process. A carbon bed with a structure similar to a sand bed removes the smell, taste, and color of organic materials and chlorine in water. During this stage, bypassing the water through active carbons, color, odor, and organic materials are absorbed. In the sand bed process, the water speed increases due to the rise in pressure and increases the filtration speed. - Clotting and coagulation process
The separation of small particles does not happen quickly on its own. Instead, the coagulation and flocculation process remove these particles. In this process, a coagulant substance neutralizes the electric charge and reduces the repulsion between suspended particles. After coagulation, flocculation occurs, causing the micron-sized flocs of suspended particles to come together and form visible particles. - Cleanable filter process
Cleanable filters automatically remove any clogging and backwash themselves. They are typically made of metal and have high corrosion resistance. One of their key features is the automatic cleaning of the filter surface when the pressure drop increases. - Ultrafiltration technology
The filtration process removes insoluble suspended particles. However, the technology comes with a high price, which has limited its use in pre-treatment. UF (ultrafiltration) membranes produce high-quality freshwater output, resulting in longer-lasting reverse osmosis membranes. UF membranes are insoluble particles with a high molecular weight. These membranes effectively separate organic and inorganic polymer molecules, colloidal particles, algae, and viruses from the incoming water.
Advantages of an industrial water purifier
The use of industrial water purifiers offers several advantages, including:
- Compared to other water desalination methods, it is more affordable
- It requires less energy than other methods.
- Unlike many desalination methods, industrial devices can operate continuously without rest.
- The process of using this device is relatively simple. Although it may initially seem complicated, mastering it will make future operations easier.
- The concentrated water produced in these devices, known as desalination wastewater, can also be reused in the environment.

Inlet water sources to the industrial water desalination device
It’s essential to consider the type of water that will enter the device. The water comes from various sources, including:
- Seawater, lake water, and ocean water are very salty and have a high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) range.
- Underground water from aqueducts and wells may have been stagnant for a long time and could be polluted. This water needs treatment and can have various TDS ranges depending on the location of the well, ranging from sweet to salty with varying hardness levels.
- Fresh surface water needs purification. It has a low TDS range but high Total Hardness (TH), which needs to be controlled.
- Surface water from rivers and springs.
Application of industrial water purification devices
As previously mentioned, the primary purpose of using a water desalination device is to produce fresh water. However, industrial water desalination devices have various other applications, including:
- Providing water for livestock and poultry
- Recycling industrial wastewater
- Generating boiler feedwater
- Producing water for pharmaceutical and cosmetic factories
- Supplying water for agricultural use
- Providing water for petrochemical, steel, textile, papermaking, dyeing, and similar industrial operations
FAQ about industrial water desalination device
Water purification removes chemical and biological pollutants from water to produce clean, healthy water. This process is essential for providing safe drinking water and is also used in industries to meet pharmaceutical, medical, animal husbandry, and agricultural needs. The purification removes suspended particles like bacteria, parasites, viruses, fungi, and moss. For more information about water purifiers and how they work, please call the numbers on the website.
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the alkalinity and acidity of a solution. Almost all drinks are acidic before any chemical activity in the body. Water has an ideal pH value. Because the reverse osmosis desalination device removes many salts from the water, the pH of the water decreases slightly.
When examining a water sample, it’s essential to consider magnesium, calcium, and sodium. Some of these substances are useful to the body, and others can be harmful. While a filtration water purifier cannot eliminate all salts, reverse osmosis water desalination can remove between 90% and 99% of pollutants. Our body primarily obtains the minerals it needs from food rather than drinking water, so it’s crucial to focus on removing toxic substances from the water.
The water obtained from reverse osmosis water desalination has a pleasant taste, high purity, and no salts, resulting in a sweet and refreshing flavor. Additionally, a reverse osmosis water desalination device is cost-effective and can operate the water purification automatically.
Repair requests for the reverse osmosis device are simple, and you can do so with just one call. Sepahan Palayesh has reliable experts to provide the best and highest quality services.
Water desalination systems are designed for a single purpose, but their filters vary. To identify the filters on your device, please send a photo and relevant information to our experts. They will send you the necessary details.
The membrane filter is the most important in reverse osmosis water desalination devices. It contains very tiny pores that effectively remove impurities such as chalk, lime, salinity, heavy metals (like arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, and mercury), nitrite, nitrate, fungi, parasites, viruses, cysts, and bacteria from water.
Reverse osmosis devices use a membrane filter and do not require a resin filter. The membrane filter effectively removes water hardness and softens the water with high precision. Moreover, it comes with low maintenance costs. However, water purification devices use a resin filter to reduce water hardness and eliminate nitrite and nitrate from water. Also, reverse osmosis devices in laboratories use membrane filters for very high filtration accuracy.
Both reverse osmosis and distillation methods reduce particles dissolved in water. In reverse osmosis, a membrane separates all water pollutants, allowing only water molecules to pass through. In distillation, like boiling, the boiled water and the obtained steam are enclosed and condensed, and finally, the distilled water is collected. The main stage of purification in this method occurs in the welding chamber. A distillation device costs less than reverse osmosis, but the subsequent costs and energy consumption of distillation are higher than reverse osmosis.
A water softener is installed at the entrance of utility systems or the house. Typically, sodium compounds like sodium polyphosphate are in water softeners. Therefore, a water softener does not affect reverse osmosis water purifiers.
